Successive rulers before and after 1947 have remained reluctant in encouraging English journalism in Jammu and Kashmir. Fighting odds, restrictions and outright denial of permissions, the English media always existed in the erstwhile state but never became the mainstay. It only started getting visible, popular and vibrant by the turn of the century, writes Nayeem Showkat

Unlike the evolution of the Urdu press in the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir, little effort has been made to assess the English press in the region.
The beginning of the English press in Jammu and Kashmir was marked with the publication of Kashmir Times, a weekly newspaper from Srinagar. Baldev Prasad Sharma and Pandit Gawsha Lal Koul are credited to have pioneered the establishment of English press in the region with the launch of Kashmir Times on November 26, 1934. Baldev Prasad Sharma co-edited the publication along with Janakinath Zutshi.
For lack of substantial evidence, it is unclear if the Kashmir Times was started by Sardar Abdul Rehman Mitha after purchasing it from BP Sharma, or was started afresh. However, what came to the fore, later on, was that a declaration in this regard was filled by Mitha. Filing a declaration is mandatory for a fresh newspaper and every time anything changes in the main declaration, owner, publisher, printer, cost, pages, language, and place of publication.

Pre-Partition Kashmir Times
Settled in Kashmir with his chaperone private secretary GK Reddy in 1944, Mitha – a Bombay Congressman – started Kashmir Times after he purchased his own press. Reddy was also operating as a Kashmir-based correspondent for the Associated Press of India. The newspaper ceased its publication during partition, as Reddy was served a notice by the District Magistrate Kashmir to leave the State of Jammu and Kashmir. Mitha and Reddy left the State on October 15, 1947, when they were halted near Domail Post, and their pockets were searched.
The government claimed they recovered some objectionable papers about a conspiracy from Reddy’s pocket and suitcase. The two men were arrested, brought back to the State and handed over to the military.
Not only Mitha, previously, Prem Nath Bazaz and Prem Nath Kana were also alleged to be involved in the conspiracy. Arrested by the police on the intervening night of October 21 and 22, 1947, both the journalists were suspected of hatching a conspiracy on the directions of the Kak administration. It was also pondered that Bazaz and Kana would be deported from the State.
Prior to this, an unknown gunman also shot at and injured Bazaz near Maisuma Police Station in April 1947. Inculpating National Conference for concocting the attack, police arrested as many as 60 people including Ghulam Nabi, a reporter of Khidmat.
In response to the attack, a meeting of members of the All–Jammu and Kashmir Press Conference was held in the office of Kashmir Times in April under the supervision of Mitha, in which the National Conference was accused of the attack.
Mitha was very critical of National Conference. Prior to this incident, Mitha and Mir Abdul Aziz of Millat and Jauhar were attacked and the blame was put on the National Conference.
In that era, the media operated in factions. In fact, a camp of newspapers was up in arms against Mitha and Reddy. When the Editor-in-Chief of Khidmat, Allama Kashfi, was arrested, the staff of Khidmat sent a memorandum to the prime minister blaming Mitha, Reddy and Aziz Kashmiri for the arrest. The issue was also discussed in the meeting of the Journalists Association.
The deportation of Mitha and Reddy could also be understood better in the backdrop of a news article published in The Khalid Kashmir on May 17, 1947, detailing that a law was passed by the Legislative Assembly of the State of Jammu and Kashmir allowing the outsiders residing in the State for 20 years to be eligible to file a declaration for starting a newspaper.
In light of this regulation, the case of the owner of the Kashmir Times newspaper and Kashmir Times Press, Abdul Rehman Mitha’s declaration being accepted by the District Magistrate Srinagar created much furore. When the declaration papers of Mitha, a resident of Bombay who had been living in Kashmir for some time, were forwarded to the Publicity Office, they were received with scepticism and the case was forwarded to the Prime Minister’s office. The papers took many years to return to the Publicity Office, following which the issue was brought to the notice of the High Court.
The court asked the District Magistrate Srinagar to state the reason behind the acceptance of Mitha’s declaration as Mitha had been residing in Kashmir for not more than five years. When the press came to know about the issue, the Kashmir newspapers started a trial against Mitha and demanded his deportation along with Reddy, his secretary, from Kashmir.
The Post-Partition Kashmir Times
Within less than a decade of the cessation of the Kashmir Times, a different one with the same title was instituted by Ved Bhasin from Delhi in the years ensuing the partition, for which, he solicited one of his friends to file a declaration. Initially, a few issues of the Kashmir Times reached Kashmir, but soon its entry was barred into the State invoking the then Customs Act and copies of the newspaper were detained at Lakhanpur.
On this, Bhasin was left with no option but to return to Kashmir to file a fresh declaration from Srinagar for the Kashmir Times. The district magistrate ordered him to furnish a security deposit of Rs 2000, an amount which was considered too much in 1954. Unable to pay the money himself, Bhasin persuaded his contractor friend in Jammu to file a declaration on his behalf.
This is how the Kashmir Times was revived as a weekly from Jammu in 1954 at the behest of Bhasin. The newspaper that turned into a tabloid for quite some time was afterwards relocated to Srinagar and then once more to Jammu.
The newspaper was converted into a daily in 1964, with Bhasin remaining to be the longest-serving editor of the newspaper for a period spanning around five decades between 1954 and 2000. JN Wali was also associated with the newspaper as an editor.

The Kashmir Chronicle
As early as 1939, an English weekly Kashmir Chronicle started publishing from First Bridge (Amira Kadal), Srinagar. It was managed by ML Koul. The newspaper belonged to Pt Gawsha Lal Koul who assumed the charge of an information officer in the government.
Koul who edited Kashmir Chronicle was alleged by the government for misusing his official position to clear the pending bills of his newspaper and using government stationery and stamps for his lengthy correspondence for the same. The newspaper was converted into a daily, but couldn’t sustain for long. The newspaper became defunct before October 1949.
According to three different articles published in the Khidmat (November 2, 1943), the Khalid Kashmir (November 19) and the Khidmat (November 11) , the editor of Kashmir Chronicle was arrested under Defence Rules in October 1943 for publishing certain allegations against an officer of Petrol Rationing. The case was brought in the court of City Munsif. He was handcuffed and paraded through the main thoroughfare.
The English Khidmat
Towards the end of 1944, the conductors of Khidmat also started an English edition of Khidmat, which couldn’t survive for long owing to certain factors. It was done in the same year when the Khidmat got converted into a daily on January 5, 1944.

Initially associated with Khidmat, ON Dhar became Assistant Editor in Khidmat (English). He later joined the state government as an information assistant and further rose to the post of secretary.
For some time, Dhar also worked as an editor in Kashmir Post, a newspaper from Jammu. It was started by Janki Nath Zutshi, an English language journalist of the erstwhile State.
Zutshi later rose to become the first Director of General Information and Broadcasting of post-1947 Jammu and Kashmir. Zutshi also edited the English weekly Kashmir Sentinel which he launched in 1941 but could survive for only two years.
As per an article published in the Khidmat on September 2, 1943, Zutshi was thrashed by a police constable near Numaish in August 1943. The editor was scheduled to meet the secretary, but the police constable refused. When Zutshi told him to inform the secretary about his arrival for a meeting, the cop lost his cool and started lashing out at him, to which Zutshi reacted, triggering a scuffle. Later, All J&K Editors’ Conference also embroiled themselves in the issue.
The Kashmir Sentinel, which was published in English till the end of 1943, changed its language to Urdu. Evading every logic, the newspaper was blacklisted in November 1943 for not registering any progress in the English language. It is in this context that the newspaper had to change its language to Urdu.
Besides, Shambhoo Nath Kaul of the Vakil also intended to make his newspaper a bilingual publication. It was on January 31, 1945, that Kaul impetrated the consent of authorities to add a few English pages to the contemporaneous volume of the Urdu weekly. The editor was granted permission as he also beseeched that he won’t demand extra newsprint for the same.
Retorting to the editor’s letter, the authorities specified that as far as the price of a single issue of the newspaper was Re 1, and the number of pages not exceeding 26 in a week, no permission was required for such a case. In addition to this conditional permission, it was also communicated to the editor that the consumption of newsprint should not exceed the allocated quota of the newspaper.
Further, the weekly Vitasta was re-launched by Bazaz in English in 1945 but it is said to have ceased its publication within a year or two. However, the name of the Vitasta is found to have been listed in the regularity statement of the local newspapers published from Srinagar for the month of August 1969.
In addition to this, another English newspaper germane to mention New Kashmir was also in circulation. The English weekly New Kashmir edited by Pt SN Tikku and owned by Pt NN Raina was published from Srinagar. It was the same time when the English newspapers emerged to flourish.
Limitations For English Newspaper
Initially, Urdu journalism flourished exponentially, though the English press was quite slow to pick up. Palpably, there were several factors behind the minimal presence of the English press in the State at that time, among which few are more conspicuous than others. The key impetuses were; the absence of a lingua franca, the literacy rate which was almost negligible, inter alia.

By then, Jammu and Kashmir was the most backward state of British India. With as less as 65,000 literates across the state, the Jammu district was comparatively better than other parts of the state, according to the Census Report of India, 1911. The literacy rate of males was 38 per mille as against one female, it is further delineated that there were only four English literate males per mille with no female.
As the Second World War ushered in, a prevalent problem of hyperinflation ensued, sparing none. The journalistic fraternity was in a state of anxiety, vis-à-vis the government’s impassive stance on their plight.
Needless to say, the prices of newsprint were skyrocketing, recording a fivefold increase within 19 months of the war. A newsprint ream selling at Rs 2 before the war cost Rs 12 during the war. So massive was the inexorable increase in the cost of newsprint that soon, the prices escalated to Rs 36 per ream, further marking an increase in the price of almost five hundred per cent and even more than that at a specific time. The enormous increase in the prices of newsprint not only resulted in its shortage, but soon the circumstances befell so worse that newsprint became utterly non-existent in the State. It had a direct bearing on the newspapers hence making the situation difficult for small newspapers.
Besides, the Jammu and Kashmir administration started classifying the newspapers of the state in 1937 during Ayyangar’s period into two categories – ‘Whitelist’ and ‘Blacklist’ – which were further classified into three groups – A-list, B-list and C-list. The advertisements and government press notes were distributed among newspapers accordingly.
Despite all these factors, according to a news article published in The Khidmat on December 18, 1937, it is estimated that there were three dozen newspapers in Jammu and Kashmir till the month of December 1937. The number, according to the Census of India 1941 increased to 44 in the spring of 1941.
The Handbook of Jammu and Kashmir State 1947 complied by the Publicity Department has recorded that Jammu and Kashmir had over 60 newspapers in 1947. However, owing to events in the backdrop of partition, all the existing English and Hindi newspapers in the erstwhile state ceased to survive. Only a dozen or so Urdu newspapers could pull through this afresh irrepressible era of un-freedom of the press.
Around 1947
Unfortunately, the pre-1947 upswing of the English press lost its vigour. By January 1, 1951, only 24 newspapers were published in the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir. In its flabbergasting feature, all 23 newspapers, except Jyoti, which was bilingual, were published in Urdu which included; four dailies, 16 weeklies and others. There was no English daily newspaper in Kashmir by this time. The English newspapers established earlier had left off owing to varied inexorable factors.
It was the same time when the amendment in section 5 (A) of the Press Act, Samvat 2008 in October 1951 was brought with an aim to curb the growth of “dummy” and “mushroom” material passing out as a newspaper. Further, the amendment was made to bring the newspapers published in the state to a minimum regularity, volume, size and standard. Notwithstanding its good intention, this amendment hit hard the sundry newspapers which were economically weak but impeccable, to the degree that most of them ceased publication for these ineluctable exigencies.
The newspapers were left with no alternative but to discontinue in the backdrop of the amendment. It was implemented by Sheikh Mohammad Abdullah’s government without seeking any suggestion from the journalist fraternity. Calling it a Black Bill, journalists across the state strongly opposed the legislation when it was still under consideration.
The Act was amended by the government at a time when only a few newspapers were able to publish, and the majority succumbed to the emergency. The amendments stated that a newspaper would be considered to have ceased printing and publishing if it printed and published less than 24 separate issues (each with a minimum of four pages and 896 square inches of printed space) for daily newspapers, and less than four issues per calendar month (each with a minimum of ten pages and 1344 square inches of printed space) for weekly newspapers.
Moreover, with the amendments to 5 (A) and the rules listed in the background, the absence of electricity during winters became a tool of censorship, leaving newspapers with no choice but to submit a new declaration as required by the prevailing press law.

The government believed that certain weekly newspapers were unable to meet their publication deadlines, particularly during the winter months. This was due to the fact that these newspapers did not own printing presses and the supply of electricity during winter was often unreliable.
As a result, newspapers sometimes remained unprinted for several days due to the lack of electricity in the press. This lack of electricity, which was often caused by the challenging geography of Kashmir, became a crucial tool for authorities to force newspapers to cease publication for not publishing enough issues in particular time frames. Primarily, it was the reason for the conversion of four to five daily newspapers into weekly newspapers.
Tragically, the Act had no saving clause which was a major issue. Later on, the government realized that section 5(A) doesn’t provide any saving clause as the newspaper has to cease publication directly and file a fresh declaration in case it wants to re-appear. There might be some other unavoidable reasons beyond the control of the printer and publisher of the newspaper for not abiding by the rules.
As a delayed follow-up, it was decided that newspapers that do not comply with the provisions of Section 5(A) will not be considered to have ceased to be printed or published, and no legal action will be taken against them until the law is amended. However, these “irregular” newspapers were barred from receiving government advertisements, court notices, and other facilities enjoyed by regular newspapers. Interestingly, the officials would “convey” to tens of thousands of tourists, mostly foreigners, that Kashmir lacks an English newspaper!
The Kashmir News
This sorry state of affairs eventually led the administration to jump in and fill the gulf. It conceived an idea to publish Kashmir News, a 4-page English daily morning newspaper from March 15, 1952. The newspaper was supposed to print the government’s publicity material, which then was perdurable in the form of pamphlets, and special and annual numbers.
This newspaper was to be issued from a hand press as no linotype machine was yet available in the erstwhile State – as per the government record – and was expected to initially follow the pattern of evening news published in Delhi. Accordingly, a proposal was moved to Prime Minister’s Office for consent.
The idea, however, could not follow the script. On November 14, 1951, the cabinet suggested information department start a four-page or less government news sheet without editorials from March 1952 for a period of nine months as an experimental measure.
The approval was entirely different from what had been proposed. With this, the idea of commencing an English daily, which would bridge the communication gap between English speakers, through the agency of the government in the State couldn’t take shape.
A Survival Issue
In 1954, newspapers like Kashmir Times, and Kashmir Post, were hitting the stands. Despite that, what makes the region quite a peculiar case in this regard is that it lacked periodicals in lingua franca for quite a long time.
The report of the Enquiry Committee on Small Newspapers, 1965 saw that the number of newspapers in the State remained almost steady during the last 10 to 20 years. The report revealed that it was only recently that owing to the easiness in filing and acceptance of declarations, new publications have emerged.
The Committee further noted that by virtue of the existing Press Law, a non-resident of Jammu and Kashmir was not permitted to file a declaration to initiate a newspaper in the State. However, it asserted that the state government at that time was ready to provide all the reasonable facilities to a bona fide non-resident Indian who wished to institute a newspaper in English or in Urdu from Srinagar or Jammu.
The Committee estimated that there were 76 periodicals being published mostly from Srinagar and Jammu in the category of small newspapers and periodicals. Barring one Hindi and one English, all the remaining newspapers of different periodicities in circulation at that time in the state were Urdu. The daily newspapers were mostly 20x3e0 cms four-sheets. The prices of the dailies varied between 10 paise and 15 paise.
The First Verification
Data available with the Registrar of Newspapers for India (RNI) reveals that the first-ever verification of a title from Jammu and Kashmir was made on December 19, 1957. As per the record, there were some 15 verifications made on the same day.
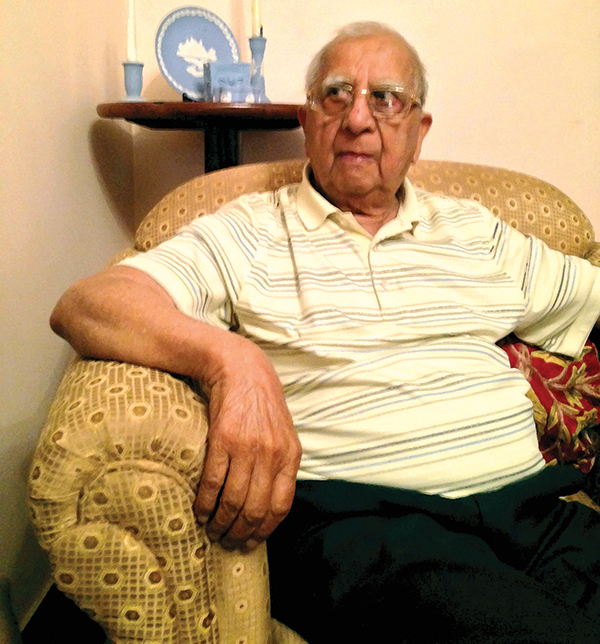

It was eight years after the establishment of RNI when noted Kashmiri historian Rasheed Taseer became the first to register a newspaper from Jammu and Kashmir. Taseer registered Muhafiz, an Urdu weekly from Srinagar in 1964. The next year, 1965, witnessed the registration of 21 new publications. Thereupon, English newspapers started hitting the stands frequently.
The following decade saw an upswing in the registration of English press in the region. The number of English newspapers and periodicals increased to 19 in 1977, according to the report of Press in India, 1977. With a total of 143 periodicals, 13 were bilingual and multilingual, five were Hindi two each were Kashmiri, Dogri and Punjabi and 100 were Urdu.
The English periodicals included; Economic Post, Srinagar; the fortnightly Education News and Views, Srinagar; Excelsior, Jammu; Jammu and Kashmir Agriculture Newsletter; Jammu and Kashmir Legislature; Jammu Express; Jammu Times; the weekly Kashmir Herald, Srinagar; the weekly Kashmir Post, Jammu; the daily Kashmir Times, Jammu; Sports Columns, Jammu; the weekly Student Express, Jammu; the weekly Student Times, Jammu; the weekly Voice of the Day, Jammu; the weekly BT-LITZ KRIEG, the weekly Young Era, Jammu, etc.
Post-1990s could be considered the golden period for the development of English journalism in Kashmir. The beginning of the twenty-first century saw English journalism become as popular in Kashmir as Urdu was.
As per the data retrieved from the official website of the RNI on March 8, 2017, 1,326 titles have been verified from Jammu and Kashmir since 1957 till the aforementioned date. The data analysis shows that out of a total of 1,326 verified titles, 1,176 periodicals have been registered so far from the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir, including Ladakh.
The RNI
The RNI was established on July 1, 1956, based on the recommendation of the First Press Commission of India. Dividing the time into six decades until 2016, the data reveals that 34 periodicals were registered in the first decade between 1957 and 1966, 169 in the second decade – 1967 to 1976, 105 in the third decade, between 1977 and 1986, 117 in the fourth decade – 1987 and 1996, 200 in the fifth decade, between 1997 and 2006, and 551 in the last decade – 2007 to 2016.

Among these 1,176 titles, 485 have been registered in English, while 447 in Urdu and 10 in Kashmiri. Out of 485 registered English newspapers, 302 were located in Jammu, 180 in Kashmir, and the remaining three in Ladakh.
The Press in India report of 2013-14 puts the cumulative circulation of the periodicals in Jammu and Kashmir at around 10 million – 9627424. Out of this, the cumulative circulation of English newspapers was more than five million – 5393275, while Urdu newspapers had a circulation of more than two and a half million – 2682839.
(The writer is a Post-doctoral Fellow in Media Studies at the Indian Council of Social Science Research, New Delhi.)