by Zeenat Farooq

Vitamin D or the sunshine vitamin is a vitamin sub-type under the class of Fat-Soluble Vitamins. It is a complex poly-hydroxy sterol by its chemical nature. It can be synthesised naturally by the action of sunlight. When sunlight hits skin, the ultraviolet radiations in it act on the underlying cholesterol and convert it into calciol (Vitamin D3), the precursor form of vitamin D. This vitamin D3 is transported to the liver where it gets converted into calcidiol (25-hydroxy vitamin D3). The kidneys then convert calcidiol into calcitriol which is the active form of vitamin D.
The term Vitamin-D is quite a misnomer because unlike other vitamins, the body has the ability of synthesising vitamin-D, which goes against the basic definition of micro-nutrients (vitamins and minerals which are required to be supplemented and cannot be synthesised within the body). Though it is quite possible to obtain the requisite amount of Vitamin-D through sun exposure, the half life of vitamin-D is short (about 2 weeks) which can lead to scarcity of body stocks, especially in winter. Therefore, it is highly likely that different people could experience vitamin-D deficiency.
Some key factors which decline the ability of our body to synthesise vitamin-D are:
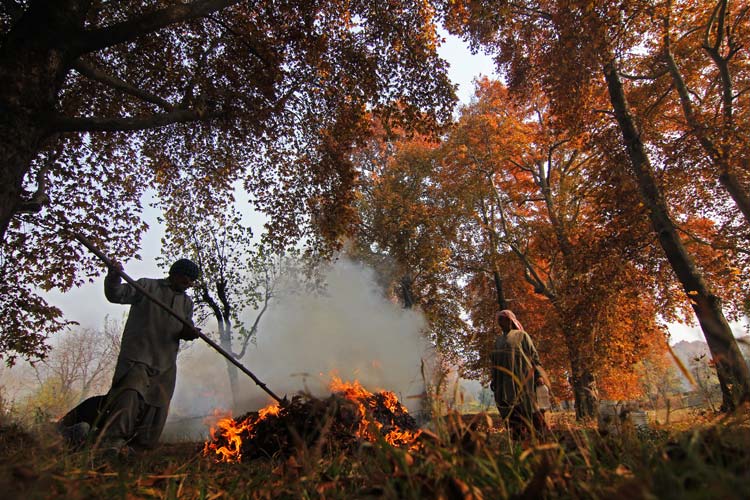
Limited sun exposure: People who stay mostly indoors are more prone to develop vitamin-D deficiency like home makers, elderly, sick, small children, people who work from home.
Skin colour: People with darker skin colour who have higher skin pigmentation are also prone to develop deficiencies.
Use of sunscreens: Sun screens shield the skin from UV radiations and therefore can reduce the ability to synthesise vitamin-D by as much as 90%.
Ethnicity: African-Americans are more prone to develop deficiency. This is because they tend to synthesise less vitamin-D due to higher skin pigmentation. Asian and Arabian Muslims are also found to have greater deficiency levels because of minimal skin exposure to sun.
Seasonal variation: Vitamin-D deficiency is more commonly observed in winter due to less sunlight and reduced daylight hours.
Use of certain drugs: The ability of vitamin-D synthesis within the body is also impaired by certain drugs which act on cholesterol, liver or kidney like statins.
Functions of vitamin D
It is very important for bones because it plays a role in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from foods and also from the kidneys into the blood, so that the latter can be used for building bones.
It has been observed in various studies that people who have optimal blood vitamin D concentrations have better tendency to combat insulin resistance and diabetic complications. Vitamin D concentrations in the blood are also found to be inversely proportional to the risk of developing type II diabetes.
Studies have established that women who are deficient in vitamin D during term have higher risks of pre-eclampsia, requirement of C-section and high risk pregnancies.
People who have sufficient amounts of vitamin D are found to be more resilient to infections like flu and influenza.
Children who have deficiency of vitamin D are more prone to allergies and asthma.
Children who have sufficient vitamin D levels are found to have normal values of blood pressure compared to children with deficiency. Vitamin D deficient children also had increased arterial stiffness which is an indicator for heart health.
It has been observed that vitamin D plays an important role in limiting the growth of blood vessels in various forms of malignant cancers. It has also been shown to play a role in limiting cell growth and cell adhesions in cancers since the vitamin is essential for maintaining cell growth and development. A recent US study shows that vitamin D might be helpful in reversal low-grade prostate tumours. A study publishes in the journal PLOS One also reports that vitamin D deficiency may contribute to incidences of leukaemia.
Vitamin-D plays role in regulating the functions of around 200 genes within the human body, all of which have critical and very diverse functions.
Vitamin D also has a protective benefit against multiple sclerosis (MS). According to a study published in the journal of Neurology, vitamin D supplementation has been used as treatment option with positive outcomes.
Oral supplementation of vitamin D can also prove beneficial against chronic heart problems. These findings were recently discussed at the American college of cardiology.
A study conducted at the University of Minnesota concludes that people with normal vitamin D levels reduce weight more effectively, with similar level of physical activity and similar diet than people who were deficient.
Daily requirements of Vitamin D
Requirements for vitamin D vary in accordance with the factors which impair its rate of synthesis. However, the general recommended guidelines for vitamin D intake, as prescribed by the US institute of medicine (IOM) published in 2010 are 400 IU for infants (0-12 months), 600 IU (1-70 years and pregnant and lactating women), 800 IU (above 70).
Fish oil and fatty fish are the richest sources of vitamin D. Chicken, eggs, milk can also provide sufficient vitamin D to meet our daily requirements.
Author is a Research Scholar at Department of Biotechnology, University of Kashmir.